Linux - Linux directory hierarchy structure
Top-Level Structure (Root Directory)
In Linux, everything starts from the root directory, which is simply:
/
From there, you’ll find several important subdirectories. Here’s a breakdown of the most common ones:
1. / – Root
-
The top of the filesystem.
-
All other directories are placed under this.
-
Not to be confused with the root user (which is
/root).
2. /bin – Essential Binaries
-
Contains basic command-line programs (like
ls,cp,rm,mv, etc.). -
These are needed even if no other parts of the system are available.
3. /sbin – System Binaries
-
Like
/bin, but for system-level tools (used by root or for system repair). -
Includes commands like
reboot,fdisk, etc.
4. /etc – Configuration Files
-
Stores system-wide configuration files.
-
For example: network settings, startup scripts, user accounts.
5. /home – User Home Directories
-
Each regular user has a personal folder here:
-
/home/student -
/home/alex
-
-
This is where your documents, downloads, and personal files go.
6. /root – Root User’s Home Directory
-
Not the same as
/ -
This is the home directory for the root user (administrator).
-
Like
/home/root, but special.
7. /var – Variable Files
-
For data that changes frequently, such as:
-
Logs (
/var/log) -
Mail
-
Print spool files
-
8. /usr – User Software and Applications
-
Contains most of the installed software, documentation, and libraries.
-
Think of it like “Program Files” on Windows.
Subfolders:
-
/usr/bin: Apps and commands for users -
/usr/sbin: Admin/system tools -
/usr/lib: Program libraries -
/usr/share: Shared data and documentation
9. /lib – Shared Libraries
-
Contains essential libraries (like DLLs in Windows) used by
/binand/sbin.
10. /tmp – Temporary Files
-
Stores temporary files created by users or applications.
-
Automatically cleared on reboot.
11. /dev – Device Files
-
Represents hardware devices as files.
-
Examples:
/dev/sda(hard disk),/dev/usb, etc.
12. /proc – Process Info
-
Virtual directory that gives real-time info about running processes.
-
Try:
cat /proc/cpuinfoorcat /proc/meminfo
13. /boot – Boot Loader Files
-
Contains the Linux kernel and files needed to boot the system.
-
Includes:
vmlinuz,initrd,grub/
14. /mnt and /media – Mount Points
-
Temporary mount points for external drives, USBs, CDs:
-
/mnt/usb -
/media/username/drive_name
-
15. /opt – Optional Software
-
Used to install third-party or optional software not managed by the package manager.
16. /srv – Service Data
-
Stores data for services like web servers or FTP servers.
-
For example: website files hosted on your system.
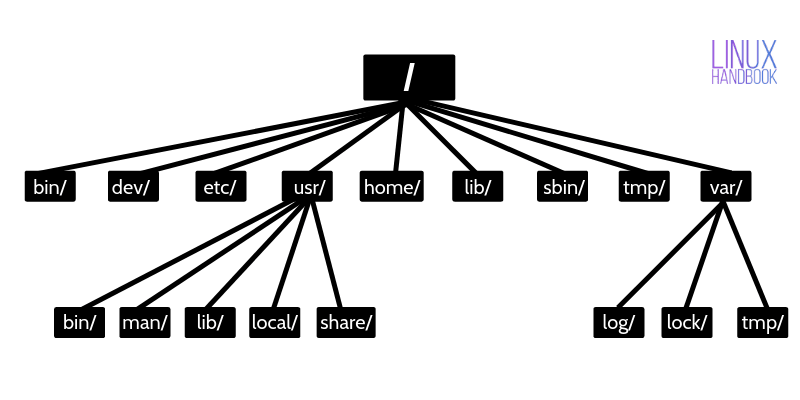
Visual diagram
Summary Table
| Directory | Purpose |
|---|---|
/ |
Root of the filesystem |
/bin |
Essential commands |
/sbin |
System/admin commands |
/etc |
System configs |
/home |
User files and folders |
/root |
Root user’s home |
/var |
Logs and variable files |
/usr |
Installed programs |
/lib |
Program libraries |
/tmp |
Temporary files |
/dev |
Device files |
/proc |
Process info (virtual) |
/boot |
Boot files and kernel |
/mnt |
Manual mount point |
/media |
Auto-mounted devices |
/opt |
Optional software |
/srv |
Server data |