XML - Data Storage and Structure
Learning Objectives
You will be able...
- ...to distinguish four data storage types and choose the right storage type for a specific project.
- ...to explain what XML is and what it is used for.
- ...to list the main properties of XML.
Introduction
Imagine producing a multimedia application with the title "The Red Deer in Switzerland" and you possess the following data (pictures, text and data table):
 Picture of Red Deer (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) Picture of Red Deer (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) |
 Describing Text (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) Describing Text (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) |
 Picture of occurence of Red Deer (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) Picture of occurence of Red Deer (Atlas of Switzerland 2.0 2004) |
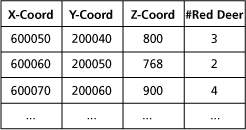 Table with Red Deer Occurence Table with Red Deer Occurence |
Before being able to start with the production of a multimedia application, the available data has to be structured and stored. Several possibilities exist to store data. We introduce you four of these possibilities in this lesson. Depending on the given data the storage method has to be chosen and applied. After this lesson, you should be able to define the best storage method for the data examples above.
A file type that is often used to store data is XML, a W3C recommendation. The main purpose of XML is to facilitate the sharing of data across different systems, particularly systems connected via the Internet. Currently, the interoperability of different datasets is considered as one of the major technological challenges within the research community. Because XML helps to solve this problem, we give you a detailed introduction to XML in this lesson.
We will show you the main properties of XML, its advantages and disadvantages. You will get familiar with the XML's syntax and the structure description of an XML document.
source: http://www.e-cartouche.ch/content_reg/cartouche/datastruc/en/html/index.html