Computer Basics - Motherboard
What Is a Motherboard?
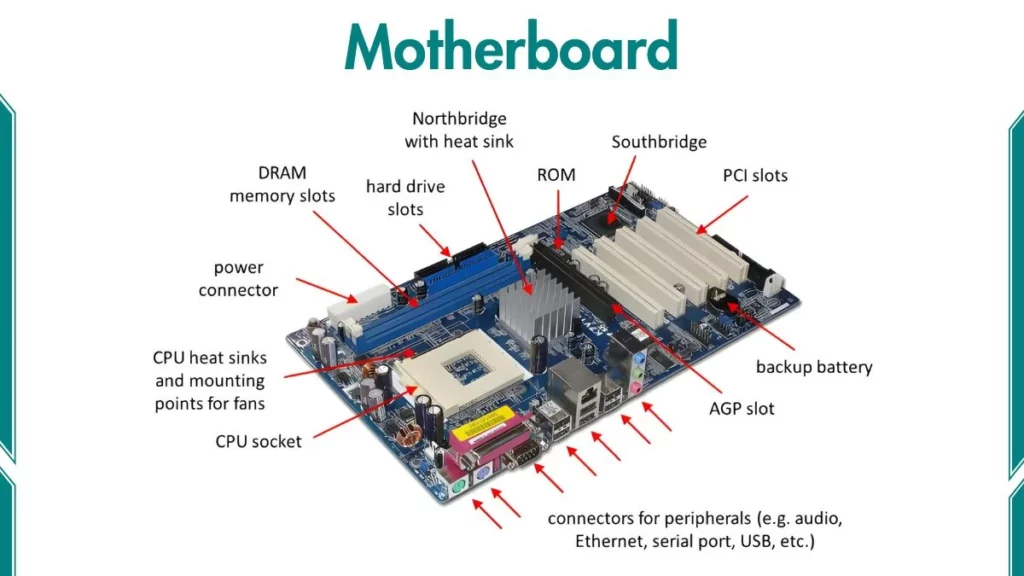
The motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer. It connects all the components of a computer together — like the CPU, memory (RAM), storage, and input/output devices — allowing them to communicate and work as one system.
It is sometimes called the system board, mainboard, or logic board (especially in Apple devices).
Functions of the Motherboard
1. Houses the CPU
-
The motherboard contains the CPU socket, where the processor is installed.
-
It supplies power and connects the CPU to the rest of the system.
2. Connects Memory (RAM)
-
RAM sticks are inserted into memory slots on the motherboard.
-
RAM temporarily stores data that the CPU uses while working.
3. Connects Storage Devices
-
Hard drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) connect to the motherboard using SATA or NVMe ports.
4. Provides Expansion Slots
-
You can add components like graphics cards, sound cards, or Wi-Fi cards using PCIe slots.
5. Handles Input/Output Ports
-
Ports for USB, HDMI, audio, Ethernet, and other devices are built into the motherboard.
6. Power Distribution
-
The motherboard distributes power from the power supply unit (PSU) to all components.
Main Components on a Motherboard
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| CPU Socket | Holds the processor |
| RAM Slots | Install memory modules |
| Chipset | Manages data flow between CPU, RAM, and devices |
| BIOS/UEFI Chip | Boots the computer and manages basic settings |
| Power Connectors | Connects to the power supply |
| Expansion Slots | For extra hardware (e.g., GPU, sound card) |
| Storage Ports | Connects SSDs, HDDs (SATA, NVMe) |
| I/O Ports | Connects peripherals (keyboard, mouse, etc.) |