Networking - Frequency Division Multiplexing
What is Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)?
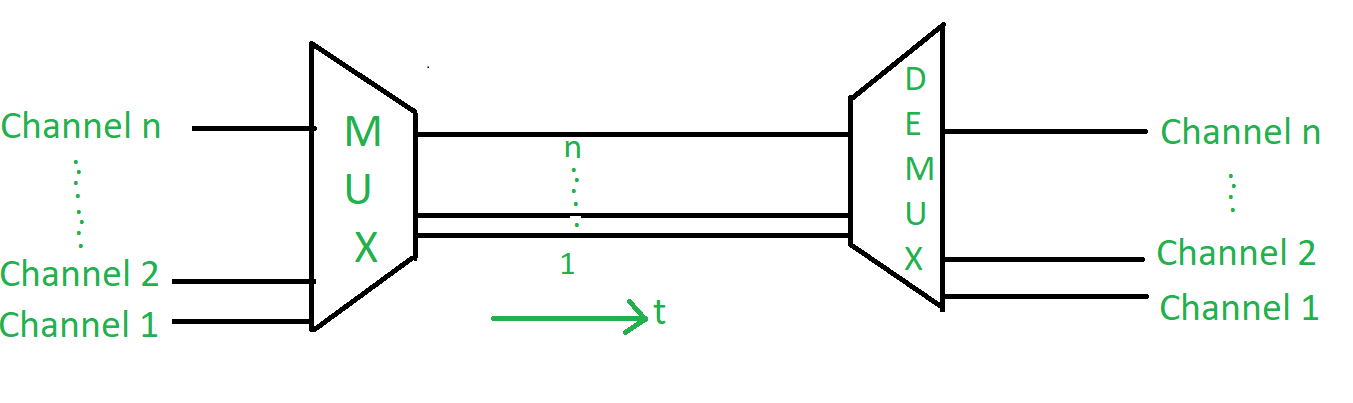
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) is a technique used in communication where multiple signals are sent at the same time over a single communication channel—by giving each signal its own frequency range (band).
It’s like giving each signal its own "lane" on a highway so they don’t interfere with each other.
Real-Life Analogy: Radio Stations
Imagine you’re listening to the radio:
-
Radio Station A plays on 91.1 MHz
-
Station B on 94.3 MHz
-
Station C on 98.3 MHz
Even though they’re all broadcasting at the same time through the air, you can tune into each one separately using their frequency.
That’s FDM in action!
How FDM Works (In Simple Steps)
-
Multiple signals (e.g., voice, data, music) are ready to be sent.
-
Each signal is assigned a different frequency band.
-
These signals are then combined (multiplexed) and transmitted over a single communication line (like a cable or airwaves).
-
At the receiver’s end, a demultiplexer separates the signals by tuning into their specific frequencies.
Key Features of FDM
-
Allows simultaneous transmission of multiple signals.
-
Used in radio broadcasting, cable TV, telephone lines, etc.
-
Requires bandpass filters to separate channels.
-
There must be guard bands (small frequency gaps) between signals to prevent interference.
Applications of FDM
-
Radio and TV broadcasting
-
Cable TV networks
-
Telephone systems (analog lines)
-
Satellite communication
-
DSL internet