Networking - Time Division Multiplexing
What is Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)?
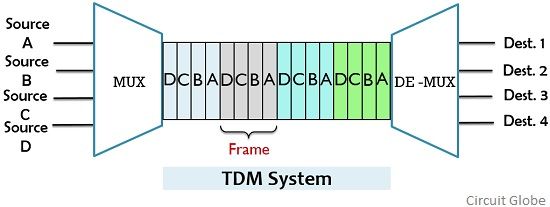
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) is a method used in communication systems where multiple signals share the same channel, but each signal gets its own time slot for transmission.
Think of it like a turn-taking system — each signal takes turns to use the channel, one after the other, very quickly.
Real-Life Analogy: School Bus Schedule
Imagine a school bus that picks up students from different houses at different times:
-
House A: 8:00 AM
-
House B: 8:05 AM
-
House C: 8:10 AM
Each student gets a specific time slot. The same bus (channel) is shared, but everyone gets their turn. That’s how TDM works!
How TDM Works (In Simple Steps)
-
Multiple signals are waiting to be sent.
-
Each signal is given a fixed time slot in a repeating cycle.
-
In each cycle, every signal gets its turn to transmit its data.
-
At the receiver’s end, the data is rearranged back into its original order based on time slots.
Types of TDM
-
Synchronous TDM:
-
Time slots are pre-assigned whether data is present or not.
-
Wastes bandwidth if some time slots are empty.
-
-
Asynchronous (Statistical) TDM:
-
Time slots are assigned only when data is ready to be sent.
-
More efficient use of bandwidth.
-
Applications of TDM
-
Digital telephone systems
-
Satellite communication
-
Fiber optic communication
-
Computer networks