Operating System - Segmentation in Operating Systems
Segmentation is a memory management technique used in operating systems to divide a program into different segments based on the logical division of a program, such as:
-
Code
-
Data
-
Stack
-
Heap
Unlike paging, segmentation divides memory logically rather than into fixed-size blocks.
-
Segment: A logical unit such as function, object, or data structure.
-
Segment Table: Keeps the base address and limit (length) of each segment.
-
Logical Address: Consists of a segment number and an offset.
-
Physical Address: Calculated by adding the offset to the segment’s base address from the segment table.
Diagram: Segmentation
Here's a neat conceptual diagram of how segmentation works:
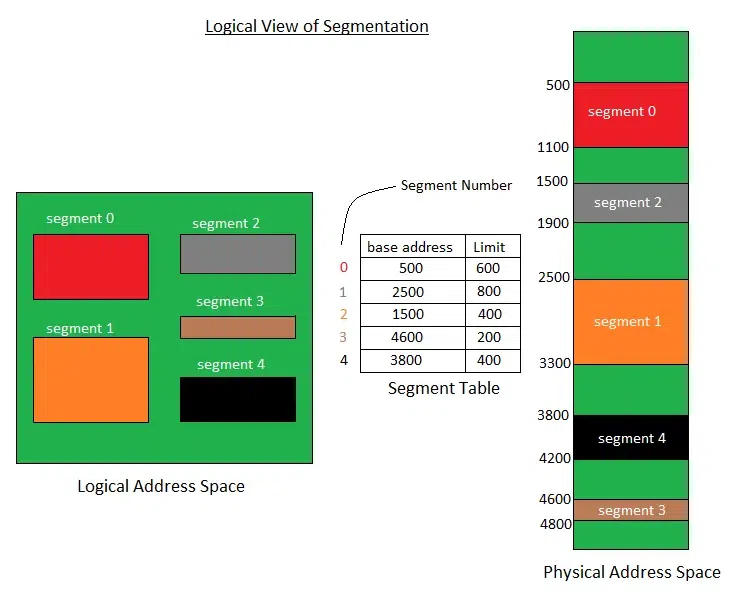
Example:
If the logical address is (Segment 2, Offset 50) and Segment 2 has a base address of 1000 and a limit of 200:
-
Check: Offset (50) < Limit (200) → Valid
-
Physical Address = Base (1000) + Offset (50) = 1050
Advantages of Segmentation:
-
Logical division of programs
-
Supports dynamic memory allocation
-
Better memory protection and sharing
Disadvantages:
-
External fragmentation can occur
-
Complex memory management